Mold thrives in damp environments and poses significant health risks, particularly for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions. Common immediate reactions include nasal congestion, sneezing, and eye irritation, while prolonged exposure can lead to severe long-term effects like fatigue, headaches, joint pain, and neurological problems. Recognizing mold allergy risks and symptoms is crucial for prompt action to mitigate health complications, especially for children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems. Mold-related respiratory issues and toxic mold sickness, caused by specific harmful molds releasing mycotoxins, require timely intervention to manage symptoms, eliminate the mold source, and control allergies or infections.
Can mold exposure trigger allergic reactions? It’s a question that arises as we navigate the often unseen dangers lurking in our environments. This article delves into the intricate relationship between mold and allergies, exploring how even invisible spores can significantly impact our health. From understanding mold exposure symptoms to identifying those at heightened risk of developing a mold allergy, we’ll uncover the far-reaching health effects of prolonged mold exposure, including respiratory issues and potentially serious conditions like mold poisoning.
- Understanding Mold Exposure and Its Impact on Allergies
- Common Symptoms of Mold Exposure
- Who is at Risk for Developing a Mold Allergy?
- Health Effects of Prolonged Mold Exposure
- Recognizing Respiratory Issues Caused by Mold
- Mold Poisoning: Signs, Causes, and Treatment
Understanding Mold Exposure and Its Impact on Allergies
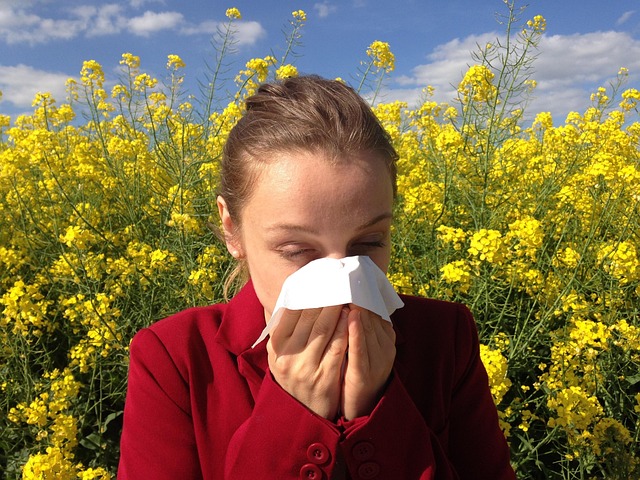

Mold thrives in damp and humid environments, making homes and buildings susceptible to its growth. Understanding mold exposure is crucial when considering its impact on allergies and overall health. When people come into contact with mold, they may experience a range of symptoms, from mild irritation to severe allergic reactions. Mold exposure symptoms can include coughing, wheezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and skin rashes. For individuals already prone to allergies or respiratory conditions, such as asthma, the risks can be even higher.
The health effects of mold are far-reaching, particularly in terms of mold related respiratory issues. Prolonged exposure can lead to chronic sinus infections, difficulty breathing, and aggravated asthma symptoms. In some cases, toxic mold sickness may occur, causing fatigue, headaches, cognitive issues, and other systemic problems. Recognizing the signs of mold poisoning is essential for prompt action, as it can prevent further health complications.
Common Symptoms of Mold Exposure

Many individuals exposed to mold may experience a range of unpleasant symptoms. Common mold exposure symptoms include nasal congestion, sneezing, runny nose, and eye irritation. Individuals with a pre-existing respiratory condition, such as asthma, may be at higher risk for developing mold-related respiratory issues, like coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Some people might also experience skin rashes or itching upon contact with moldy areas.
Beyond these immediate reactions, prolonged exposure to toxic mold can lead to more severe health effects. Signs of mold poisoning may include fatigue, headaches, memory problems, and a general feeling of ill health. In some cases, individuals suffering from toxic mold sickness might experience joint pain, muscle weakness, and even neurological symptoms. It’s important to recognize these potential mold allergy risks and health effects, as prompt action can help mitigate the negative consequences associated with mold exposure.
Who is at Risk for Developing a Mold Allergy?

Anyone can potentially develop a sensitivity or allergy to mold, but certain individuals are at higher risk. People with a history of allergies, asthma, or other respiratory conditions are more susceptible to mold-related health issues. Children, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems may also be more vulnerable to the adverse effects of mold exposure. Living or working in areas with high moisture levels, persistent leaks, or water damage can increase exposure to mold spores, thereby elevating the risk of developing a mold allergy and experiencing related symptoms like runny nose, sneezing, itchy eyes, and difficulty breathing.
Health Effects of Prolonged Mold Exposure
Prolonged exposure to mold can have severe health effects, especially for individuals already susceptible to allergies or respiratory conditions. Mold exposure symptoms range from mild to severe and can affect multiple systems in the body. Those with mold allergy risks are particularly vulnerable; they may experience exacerbated symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and asthma attacks. Prolonged exposure might lead to more serious health effects, including mold-related respiratory issues, such as chronic sinus infections and bronchitis.
In extreme cases, toxic mold sickness can occur when individuals are exposed to high levels of harmful molds, like Aspergillus or Stachybotrys. This condition is characterized by a range of symptoms, from headaches and fatigue to coughing, wheezing, and in severe instances, neurological issues. It’s crucial to address any signs of mold poisoning promptly, as these indicators—like persistent cough, skin rashes, memory loss, and dizziness—can be early warning signs of more serious health complications stemming from prolonged exposure to the toxic molds that can thrive in damp environments.
Recognizing Respiratory Issues Caused by Mold

Recognizing Respiratory Issues Caused by Mold
Exposure to mold can lead to a range of respiratory issues, especially for individuals with pre-existing conditions like asthma or allergies. The symptoms of mold exposure may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and nasal congestion. These problems often arise due to the tiny mold spores that circulate in the air, which can be inhaled into the lungs, triggering allergic reactions or exacerbating existing respiratory ailments.
Understanding the health effects of mold is crucial when considering mold allergy risks. Prolonged exposure to toxic mold can result in what’s known as “mold poisoning” or “toxic mold sickness.” This condition manifests through symptoms such as fatigue, headaches, skin rashes, and cognitive issues. In severe cases, it may even lead to neurological problems. Recognizing these mold-related respiratory issues is vital for prompt intervention and mitigating the potential risks associated with mold exposure.
Mold Poisoning: Signs, Causes, and Treatment

Mold Poisoning: Signs, Causes, and Treatment
Mold poisoning, also known as toxic mold sickness, can occur when individuals are exposed to harmful molds in their environment. The health effects of mold vary widely, but severe cases can lead to significant respiratory issues, especially for those with pre-existing conditions or compromised immune systems. Mold exposure symptoms may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness—signs indicative of mold-related respiratory problems.
The causes of mold poisoning are primarily linked to prolonged or high levels of exposure to toxic molds, such as Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Cladosporium. These molds can produce harmful compounds, including mycotoxins, which, when inhaled, may cause a range of adverse health effects. Treatment for mold poisoning typically involves addressing the symptoms, removing the source of mold from the environment, and in some cases, medication to manage allergies or infections. Prompt action is crucial to mitigate long-term health risks associated with mold exposure and allergy risks.