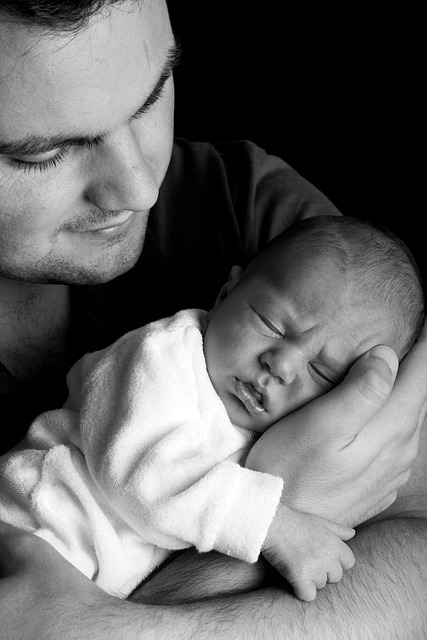
Oregon's robust child welfare legal framework prioritizes child safety and well-being through structured statutes and regulations. Navigating these laws is crucial for stakeholders, from social workers to parents, as they define jurisdiction and protect both children and families. Key aspects include dependency proceedings, reporting suspected abuse, specific rights for children and parents in foster care, court decisions on placement, and meticulous protocols for temporary placements, foster care, and adoptions, all aimed at long-term stability for Oregon's youth.
Oregon’s child welfare legal framework is a complex web designed to protect vulnerable children while respecting the rights of families. This article guides you through key aspects of navigating Oregon’s child welfare laws, covering jurisdiction, reporting requirements, foster care rights, court involvement, and placement/adoption procedures. Understanding these components is crucial for both professionals and parents involved in the process, ensuring every child receives safe, permanent housing.
- Understanding Oregon's Child Welfare Jurisdiction
- Legal Requirements for Reporting Suspected Abuse
- Rights of Children and Parents in Foster Care
- The Role of Courts in Child Welfare Cases
- Navigating Placement and Adoption Procedures
Understanding Oregon's Child Welfare Jurisdiction

Oregon, with its robust child welfare legal framework, provides a structured approach to safeguarding the well-being of children within its borders. Navigating child welfare laws is essential for all stakeholders, from social workers to parents and guardians. The state’s jurisdiction in this area is defined by a comprehensive set of statutes and regulations designed to protect vulnerable youth and ensure their access to necessary resources.
Understanding Oregon’s child welfare system involves grasping key legal concepts such as dependency, neglect, and guardianship. Dependency proceedings are initiated when a court determines that a child cannot safely reside with their parent or guardian, triggering a process aimed at reunification or permanent placement. This intricate legal landscape offers a web of protections, ensuring that the rights of both children and families are respected while prioritizing their overall welfare.
Legal Requirements for Reporting Suspected Abuse

In Oregon, the reporting of suspected child abuse is a critical aspect of protecting vulnerable youth and adhering to the state’s stringent child welfare legal framework. Individuals who come into contact with children are legally required to report any reasonable suspicion or knowledge of physical, sexual, emotional, or neglectful abuse to the Department of Human Services (DHS). This includes parents, caregivers, educators, healthcare providers, and other professionals interacting with minors.
Navigating child welfare laws can be complex, but it’s essential for everyone in Oregon to understand their obligations. Failure to report suspected abuse may result in legal consequences. The state’s laws prioritize the safety and well-being of children, and by adhering to these reporting requirements, individuals contribute to a robust system designed to intervene and support at-risk youth.
Rights of Children and Parents in Foster Care

In Oregon, both children and parents have specific rights within the foster care system, which are protected by state law. Children in foster care retain their fundamental rights, including the right to privacy, due process, and access to education and healthcare. They also have the right to be heard and involved in decisions affecting their lives, fostering a sense of agency despite their circumstances. Parents or guardians, on the other hand, are entitled to reasonable visitation and communication with their children in foster care, as well as the right to challenge any termination of parental rights through legal representation.
Navigating child welfare laws can be complex, but these rights ensure that both children and parents receive fair treatment during this challenging period. Legal advocates play a crucial role in assisting families in understanding and exercising their rights, ensuring a just process for all involved.
The Role of Courts in Child Welfare Cases

Oregon’s courts play a pivotal role in navigating the complex landscape of child welfare laws, ensuring the safety and well-being of vulnerable children. When child protection services intervene, the judiciary is tasked with making critical decisions that can shape a child’s future. Judges must carefully review evidence, assess risks, and determine the most suitable arrangements for a child’s placement and care.
These legal proceedings involve a delicate balance between protecting the rights of both the child and their family while prioritizing the child’s best interests. Courts work in conjunction with child welfare agencies to create temporary or permanent solutions, such as fostering homes, adoption, or reuniting families, always guided by the overarching goal of promoting stability and growth for the child.
Navigating Placement and Adoption Procedures
Navigating Oregon’s child welfare laws involves understanding complex procedures for placement and adoption. The state prioritizes the safety and well-being of children, with a comprehensive legal framework designed to ensure secure transitions for those in need. This process is guided by strict regulations that manage temporary placements, foster care, and eventual adoptions, ensuring every step aligns with the best interests of the child.
For placement, social workers must follow specific protocols, including thorough assessments and matching criteria, to connect children with suitable families or group homes. Adoption proceedings are equally meticulous, involving legal processes that safeguard the rights of biological parents while facilitating new family formations. These procedures emphasize transparency, accountability, and a commitment to long-term stability for Oregon’s youth.
